
What is Agile Project Management?

Introduction

Agile project management is a systematic, phase-by-phase approach to project delivery that adheres to the life cycle of a project. Iterative processes are commonly used in software development projects because they promote speed and flexibility. Agile teams execute concurrent project phases, called “agile sprints” or iterations. These allow you to solve issues and make ongoing adjustments while responding quickly to outcomes, customer feedback, and results.
Project Management Certification: Learning through Failures
Enrolling in a project management certification like PMP or Agile project management credentials provides a valuable context for understanding failure within a broader educational scope. These certification courses frequently incorporate case studies of unsuccessful projects, allowing learners to analyze real-world scenarios and lessons learned from failed projects. This educational approach is indispensable for honing robust project management tools and techniques.
For those aspiring to stay ahead of the curve, VERSAtile Reads presents “Mastering Project Management – Exam-Cram Essentials.” This agile project management book goes beyond conventional curriculum and instruction guides, offering a quick overview to reinforce your project management knowledge and excel in certification exams.
What is Agile Project Management Certification?
Agile Project Management Certifications attest to a person’s proficiency in using Agile methods and concepts in project management. Agile project management is a fluid, iterative process that prioritizes client happiness, cooperation, and flexibility. It has been embraced by many sectors, including software development, to manage projects with shifting priorities and objectives.
Several master’s degrees in curriculum and instruction online are available, and professional organizations and training providers typically offer them. Some of the well-known Agile Management certifications include:
- Certified ScrumMaster (CSM): Offered by Scrum Alliance, this certification focuses on the Scrum framework, one of the most popular Agile methodologies.
- Professional Scrum Master (PSM): Provided by Scrum.org, the PSM certification also focuses on Scrum principles but is not tied to a specific training course.
- Agile Certified Practitioner (PMI-ACP): Offered by the Project Management Institute (PMI), this certification covers a broad range of Agile methodologies, including Scrum, Kanban, Lean, and others.
- Certified Agile Project Manager (IAPM): Provided by the International Association of Project Managers, this certification covers Agile project management concepts and techniques.
- SAFe Agilist (SA): This certification, offered by Scaled Agile, is focused on the Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe), designed for large-scale Agile implementations.
- Disciplined Agile Scrum Master (DASM): Provided by the Disciplined Agile Consortium, this certification combines elements of Agile, Scrum, and lean thinking.
Factors like certifying bodies and specific courses influence Agile Project Management certification cost. For instance, Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) may range from $1,000 to $1,500, Professional Scrum Master (PSM) exams are around $150, Agile Certified Practitioner (PMI-ACP) costs about $435 to $495, and SAFe Agilist is priced between $995 to $1,295. Agile Project Management Course Online Courses are available on platforms like Udemy, Coursera, LinkedIn Learning, Scrum Alliance, Scaled Agile, and PMI. Prices for online courses range widely, from $50 to several hundred dollars, and factors include course content, instructor reviews, and alignment with specific Agile certifications.
What is the Agile Method Of Project Management
Agile project management divides work into manageable chunks. These project components are finished in days or weeks-long sprints. These workshops cover everything from the first stages of design to testing and quality control (QA).
Teams may release finished parts as they go, thanks to the Agile approach. Teams can show that these portions are adequate with this continuous release plan, and if not, they can swiftly address any issues. The idea is that since there is constant improvement throughout the project lifespan, this lowers the likelihood of significant failures.
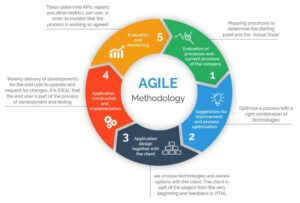
How APM Works?
Agile teams use best practices for quality assurance, fast feedback, and continuous change in their iterations. Using technology that automates processes, they embrace methodologies like continuous integration and deployment to accelerate the delivery and usage of products. Agile project management also requires teams to assess progress in terms of time and money regularly. They measure their work using velocity, burndown, and burnup charts rather than Gantt charts and project milestones to monitor their progress.
Agile project management life cycle doesn’t require the presence or participation of a project manager. While a project manager oversees the money, staff, project scope, and other crucial components under conventional project delivery approaches like the Waterfall model, the project manager’s function is not as important as it once was.
Specific Agile approaches add other layers of management. The Scrum approach, for example, calls for a Scrum Master who helps set priorities and guides the project through to completion.
What Are the Five Agile Project Management Model Phases?
Agile project management life cycle phases include:
- Envision: In this phase, the demands of the final clients are determined, and the project and overall product are initially conceptualized. In this phase, the project’s stakeholders and personnel are also decided.
- Speculate: This phase focuses on creating the product’s basic needs. Teams will collaborate to develop a feature list for the finished product before deciding on project milestones.
- Explore: While adhering to project limitations is the primary goal, teams will also look into other options to complete project needs. Before going on to the next milestone, teams work on individual ones and iterate.
- Adapt: The outcomes are reviewed, and teams make any necessary adjustments. This stage focuses on adjustments or modifications according to staff and client input. Continuous feedback is necessary to ensure that every project component satisfies end-user needs. With every iteration, the project ought to get better.
- Close: The outcomes are reviewed, and teams make any necessary adjustments. New requirements are used to gauge the final project’s performance. Errors or problems that arise during the process should be examined to prevent them from happening again.
Agile Project Management Benefits
Agile project management proponents assert that the methodology has many advantages, such as the following:
- More freedom: Due to project management, designers can work on models that match their strengths.
- Efficient use of resources: This makes deployment quick and waste-free.
- Greater flexibility and adaptability: Developers can make better modifications and customizations.
- Rapid detection of problems: This makes better project management and speedier corrections possible.
- Increased collaboration with users: Products, as a result, better satisfy consumer needs.
- Differences from other project management methods: APM requires less upfront definition of objectives and procedures than classic project management techniques, such as Waterfall.
Responsibilities of Agile Project Managers
The project manager’s position in Agile techniques changes from that of a typical manager to that of a facilitator and servant leader. Depending on the particular Agile framework or technique being used (e.g., Scrum, Kanban, etc.), the duties of Agile project managers may differ; nonetheless, some regular duties comprise:
- Facilitate and support Agile ceremonies and processes, such as Sprint Planning, Daily Stand-ups, Sprint Reviews, and Sprint Retrospectives.
- Empower and enable the Agile team to self-organize and make decisions collaboratively. Encourage a culture of accountability and ownership within the team.
- Identify and remove impediments or obstacles that hinder the team’s progress. This could involve addressing issues related to resources, dependencies, or other productivity factors.
- Act as a liaison between the Agile team and external stakeholders, facilitating communication and ensuring the team has the necessary resources and support.
- Work together to prioritize tasks, establish and manage a product backlog, and help determine the level of effort assigned to each backlog item. This includes participating in release planning and helping the team set realistic goals.
- Collaborate with organizational stakeholders to manage project budgets and allocate resources effectively. This may involve tracking costs and resource utilization throughout the project.
Agile Project Management Best Practices
The key components of agile project management best practices include adaptability, teamwork, and client satisfaction. A minimum viable product (MVP) should be delivered as the primary focus of all essential practices, including cross-functional teams, iterative development, customer involvement, daily stand-up meetings, prioritization, adaptability, continuous integration, collaborative decision-making, visual management, retrospectives, and a sustainable pace. Regular feedback, honest communication, and cultivating a continuous improvement culture are emphasized. Agile seeks to build self-organizing teams that adapt to shifting needs and provide value incrementally while preserving high customer satisfaction and product quality.
Conclusion
In conclusion, software development frequently uses Agile Project Management (APM), a systematic and iterative approach to project delivery. Agile sprints are used, which enables teams to react instantly to customer feedback and project results. APM’s five phases—Envision, Speculate, Explore, Adapt, and Close—strongly emphasize adaptability and ongoing development. Although APM has more flexibility, more effective use of resources, and improved teamwork, it may also have disadvantages, such as uneven outcomes and challenges in tracking advancement. Agile project managers enable teams to self-organize by acting as facilitators and servant leaders. Agile methodologies like Scrum, Extreme Programming, and Adaptive Software Development offer flexible solutions. The secret to APM’s success is balancing its benefits and drawbacks while matching organizational requirements and project objectives.
FAQs
1. What is agile project management?
Answer:
A software development process known as “agile project management” strongly emphasizes regular releases and the iterative integration of user feedback.
Software teams can collaborate more broadly, grow more quickly, and become better at adapting to changing market conditions using agile project management practices.
2. What is agile project management certification?
Answer:
Agile Project Management Certification is a credential obtained through programs such as Certified ScrumMaster (CSM), Professional Scrum Master (PSM), PMI Agile Certified Practitioner (PMI-ACP), SAFe Agilist, and DSDM Agile Project Leader. These certifications validate an individual’s understanding and application of Agile project management principles, emphasizing collaboration, iterative development, and adaptability to change. Offered by various organizations, these certifications often require training, exams, and practical experience to ensure individuals possess the knowledge and skills necessary for effective Agile project management. While certification can enhance credibility, practical experience, and ongoing learning remain essential for becoming a proficient Agile practitioner.
3. What is Scrum Project Management?
Answer:
Scrum is an Agile project management framework primarily used in software development. It emphasizes iterative and incremental development, focusing on delivering small, functional pieces of a product in short time frames, known as sprints (usually 2-4 weeks). Scrum involves cross-functional teams, with roles like Scrum Master, Product Owner, and Development Team. Daily stand-up meetings, regular sprint planning, and retrospective meetings are critical components of Scrum.
4. What is Waterfall Project Management?
Answer:
Waterfall represents a conventional project management methodology marked by its linear and sequential approach. Within Waterfall, projects are segmented into discrete phases: requirements, design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance. Each phase necessitates completion before progression to the subsequent phase, and incorporating changes becomes difficult once a phase is concluded. This methodology follows a structured, plan-driven path, commonly applied to projects with clearly defined requirements and minimal anticipated alterations.
5. What is the Agile Manifesto in Scrum?
Answer:
The Agile Manifesto in Scrum is a guiding philosophy for software development teams practicing agile project management and creating innovative products. It emphasizes collaboration, adaptability, customer satisfaction, and iterative development.
6. Is agile project management certification worth it?
Answer:
Yes, an agile project management certification is valuable for those seeking to advance their careers in project management, particularly in industries like software development, where Agile methodologies are prevalent. Certification demonstrates a commitment to mastering Agile principles and practices, which can enhance job prospects and earning potential. Additionally, certification programs often provide valuable knowledge and skills that can be applied in various project management roles, making them a worthwhile investment for professional development.
- Published Date:



