
DevOps Essentials: How to Automate Your Workflow Effectively

Introduction
In today’s fast-paced tech environment, DevOps has become the backbone of agile software development. By merging development and operations, organizations can deliver better products faster, more reliably, and with fewer errors. A core pillar of DevOps success? Automation.
However learning DevOps automation tools like Jenkins, Docker, Kubernetes, Ansible, and Terraform can be overwhelming, especially when preparing for certifications.
That’s where VERSAtile Reads helps. With expertly designed practice questions, exam cram notes, and study guides, VERSAtile Reads is your go-to platform for mastering DevOps and passing certifications with confidence.
Understanding DevOps: A Brief Overview
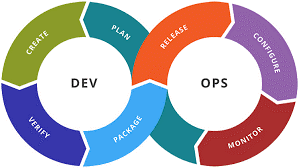
DevOps is a new process that unifies software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) into a single method of software delivery. DevOps fosters collaboration, continuous improvement, and the removal of manual, error-ridden processes.
The major objectives of DevOps are:
- Speeding up time to market
- Enhancing product quality
- Facilitating team collaboration
- Decreasing operational risks
Through adopting DevOps practices, teams can dismantle silos, raise transparency, and synchronize business goals with technical implementation.
Why Automation is the Core of DevOps
Automation isn’t a technical aspect of DevOps, it’s essential to its success. Without automation, DevOps is merely a theoretical, not a practical concept. Manual operations create inconsistencies, deployment delays, and engineers burn out. Automation fixes all these issues by speeding up workflows, making them more predictable, and making it easier to scale.
Advantages of Automation in DevOps
- Consistency: Automated processes remove the possibility of human error and provide repeatable results.
- Speed: Repetitive tasks such as testing, deployment, and configuration are carried out faster.
- Scalability: Automation allows operations to scale without increasing manual overhead.
- Focus: Eliminating tedious tasks frees teams up to innovate and think about problems.
To successfully utilize DevOps automation, it is vital to realize where automation provides the greatest value. The following are the central areas where automation is typically utilized in DevOps processes.
1- Continuous Integration (CI)
Continuous Integration is the process of automatically merging code changes made by numerous contributors to a common repository. CI makes sure that code is tested and verified continuously, which minimizes integration problems and enhances collaboration.
Automation in CI encompasses:
- Code commits initiating automated builds
- Unit tests run on each push
- Automatic alerts on failed builds
- Jenkins, Travis CI, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, and CircleCI are popular CI Tools
2- Continuous Delivery and Continuous Deployment (CD)
CD takes CI one step further by automating the process of release, allowing teams to push software into staging or production environments whenever they want. Whereas Continuous Delivery involves manual approval prior to deployment, Continuous Deployment allows the complete pipeline right through to production automation.
Advantages of CD automation:
- Faster, safer releases
- Immediate feedback loops
- Decreased rollback hazards
- Tools to Consider: Spinnaker, Argo CD, Octopus Deploy, Azure DevOps Pipelines
3- Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
IaC provisions and manages infrastructure through code instead of manual settings. With IaC, environments are reproducible, version-controlled, and consistent.
Automation tasks in IaC:
- Provisioning virtual machines, databases, and networks
- Handling cloud resources declaratively
- Automating setup of the environment for development, testing, and production
- Tools: Terraform, AWS CloudFormation, Pulumi, Ansible
4- Configuration Management
Configuration management keeps systems in the right state across environments. It prevents configuration drift and facilitates standardization.
Automated tasks include:
- Installing packages and services
- System file and user management
- Applying the same configuration to servers
- Leading Tools: Chef, Puppet, Ansible, SaltStack
5- Monitoring and Observability
Automated monitoring tools keep applications and infrastructure healthy. They report metrics, create logs, and raise alerts according to defined criteria.
Why automate monitoring?
- To catch problems early
- To ensure high availability
- To respond to failures proactively
- Tools to Use: Prometheus, Grafana, ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana), Datadog
Step-by-Step Guide to Automating Your DevOps Workflow
Step 1: Map Your Current Workflow
Start by writing down your present development and operations workflow. Determine repetitive, manual tasks within coding, testing, building, deploying, and monitoring.
Questions to Ask:
- Which processes take the longest time?
- Where are mistakes most likely to happen?
- Which tasks can be templatized or standardized?
Step 2: Choose Automation Tools That Fit Your Stack
Select tools that play nicely with your existing technology stack and align with your team’s goals. Begin with minimal necessary tools and don’t be afraid of complexity.
Example toolchain:
- Git for source control
- Jenkins for CI/CD
- Docker for containerization
- Kubernetes for orchestration
- Terraform for infrastructure
Step 3: Create a CI/CD Pipeline
Automate testing, packaging, and deploying code. Establish your stages in your workflow pipeline, such as:
- Code checkout
- Automated testing
- Artifact creation
- Deploying to staging or production
Step 4: Automate Infrastructure with IaC
Create your cloud resources and networking elements with infrastructure templates. Version-control these templates and have them in your repository.
Best Practices:
- Utilize modular and reusable code
- Secure credentials with secret management tools
- Inspect and test changes within staging environments prior to production deployment
Step 5: Add Automated Testing
Use several layers of testing:
- Unit testing: Test small units of code
- Integration testing: Make modules interact correctly
- End-to-end testing: Imitate real-world user behavior
- Run these tests in your CI pipeline to check code quality at each stage.
Step 6: Deploy Monitoring and Alerting Systems
Implement monitoring tools to gather real-time information regarding your systems. Set up alerts for:
- High error levels
- CPU and memory consumption spikes
- Sluggish response times
- Make logs and metrics readable by both development and operations teams.
Step 7: Continuously Improve and Iterate
DevOps is a cyclical process. Periodically review your automation strategy, gather feedback from your team, and refine based on performance data and evolving requirements.
Best Practices for DevOps Automation
- Begin with rapid wins: Automate low-complexity, high-impact activities to get started quickly.
- Document first: Document pipelines, configurations, and workflows to share.
- Have the whole team on board: Foster collective responsibility for automation across roles.
- Version control everywhere: Follow changes to scripts, configurations, and templates.
- Lock down your pipelines: Enforce DevSecOps practices, such as secrets management and vulnerability scanning.
DevOps Automation and Career Development
By mastering DevOps automation, you open yourself to a broad range of career choices in cloud, infrastructure, and software development.
Hirable roles include:
- DevOps Engineer
- Site Reliability Engineer (SRE)
- Cloud Engineer
- Automation Engineer
- Build and Release Manager
Crucial skills to develop are:
- Scripting (Bash, Python)
- CI/CD tool working
- Knowledge of cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, GCP)
- Knowledge of containers and orchestration
Why Choose VERSAtile Reads for DevOps Certification Prep?
Studying DevOps can feel like drinking from a firehose, too much information, too fast. That’s why VERSAtile Reads breaks it down into bite-sized, exam-focused learning modules.
We provide:
- Exam Cram Notes – Condensed content to help you revise efficiently.
- Practice Questions – Modeled after real exam formats to boost your confidence.
- Current Exam Blueprints – Our materials are constantly updated to match the latest certification standards.
Whether you’re a working professional or a student preparing for your first DevOps certification, VERSAtile Reads gives you the tools to succeed.
Conclusion
Automation is not only a DevOps feature, but its very core. By automating your workflow efficiently, you reduce mistakes, speed up innovation, and guarantee stable delivery pipelines. From provisioning infrastructure to monitoring an application, every automated activity plays a role in creating a more agile, robust, and team-oriented software development lifecycle.
At VERSAtile Reads, we believe in empowering students to master contemporary IT practices. With the right strategy, tools, and attitude, you can make the most of DevOps automation to boost efficiency and tap into new career prospects.
FAQS
1- Is prior experience necessary to learn DevOps automation?
No. DevOps embraces learners from development and operations backgrounds alike. Newcomers can begin with core tools such as Git, CI/CD platforms, and progress to scripting, cloud platforms, and IaC slowly.
2- What is the difference between Continuous Delivery and Continuous Deployment?
Continuous Delivery requires manual approval before deploying to production, while Continuous Deployment automates the entire process, pushing updates directly to end users without manual intervention.
3- Is it necessary to use containers like Docker for DevOps automation?
While not mandatory, containers offer significant benefits in DevOps workflows, such as consistency across environments, simplified deployments, and easier scalability. They are widely used alongside orchestration tools like Kubernetes.
- Published Date:



