
Cloud Foundations: What Every Beginner Should Know

Cloud Foundations: What Every Beginner Should Know
Introduction
The fast pace of technological development has revolutionized the way humans and organizations store, manipulate, and retrieve information. Cloud computing, one of the greatest innovations of the 21st century, is a term that has revolutionized the manner in which companies conduct business and human beings engage with online resources. For starters entering the realm of IT, knowledge of cloud computing is no longer a luxury, it is necessary.
At VERSAtile Reads, we believe in transforming complex topics into clear, practical insights. Whether you’re a student, an aspiring IT professional, or simply curious about the cloud, our Cloud Foundation certification exam prep resources equip you with the essential concepts, key benefits, and best practices of cloud computing and cloud certifications.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the provision of computing services such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics over the internet (“the cloud”). Rather than having to own and run their own physical servers, users can lease or subscribe to these resources on-demand from cloud providers.
These resources are located in off-site data centers and can be accessed via web browsers, applications, or APIs. Cloud computing allows users to scale services dynamically, pay as they go, and quickly and easily deploy applications.
Key Characteristics of Cloud Computing
In order to grasp cloud foundations well, beginners must acquaint themselves with five important features that determine cloud computing:
- On-Demand Self-Service
End users are able to use computing resources automatically without the intervention of humans from the service provider.
- Broad Network Access
Cloud services are delivered over the internet via standard hardware like laptops, smartphones, and tablets.
- Resource Pooling
Multiple users share resources that are pooled together, with allocation on-demand.
- Rapid Elasticity
Cloud resources can be scaled rapidly in accordance with workload needs.
- Measured Service
Usage is metered, monitored, and reported, which brings transparency to both the provider and consumer.
These features help organizations improve efficiency, reduce IT expenses, and drive innovation.
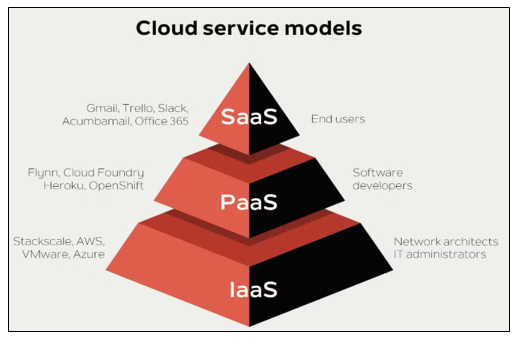
Common Cloud Service Models
Understanding the basic cloud service models – IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, is essential for any beginner in cloud computing. These models offer varying levels of control, flexibility, and management.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS delivers virtualized computing resources over the internet. Users can manage operating systems, storage, and deployed applications, while the underlying infrastructure is handled by the provider.
Popular IaaS providers: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Example: Hosting a website using virtual machines and cloud-based storage.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides a ready-to-use environment for developers to build, test, and deploy applications without managing the underlying hardware or system software. It accelerates development by handling infrastructure setup automatically.
Example: Developing applications using Google App Engine or Azure App Service.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription or pay-per-use basis. Users simply access the application through a web browser without worrying about installation or maintenance.
Example: Gmail for email, Microsoft 365 for collaboration, and Salesforce for customer relationship management.
Advantages of Cloud Computing for Newbies and Organizations
- Cost Savings
Cloud computing obviates the expense of investing in expensive hardware and infrastructure. Pay-as-you-go pricing schemes enable organizations and individuals to scale up or down as required, maximizing IT expenditure.
- Scalability and Flexibility
Whether it’s a blog or an enterprise application, the cloud enables you to scale resources as needed without manual intervention or downtime.
- Reliability and Disaster Recovery
Cloud platforms offer built-in backup, disaster recovery, and data replication services, ensuring business continuity in the event of hardware failure or data loss.
- Enhanced Collaboration
Cloud-based applications enable real-time collaboration across different locations and devices, making teamwork seamless and efficient.
- Accessibility and Mobility
With cloud computing, users can access files, applications, and tools from anywhere in the world—supporting remote work, global collaboration, and 24/7 productivity.
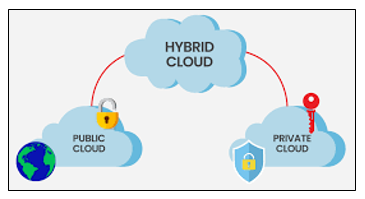
Cloud Deployment Models
Beginners must also know the three main deployment models employed for deploying cloud environments:
- Public Cloud
Third-party-provided services for public use. Example: Amazon Web Services (AWS).
- Private Cloud
It is exclusively utilized by one organization, frequently housed on-premises. Provides greater security and control.
- Hybrid Cloud
Mixes public and private clouds to enable data and applications to be shared between them. This method provides flexibility as well as optimized resource use.
Popular Cloud Providers
Understanding top cloud platforms is important for developing a core understanding. The providers listed below are market leaders:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): Provides an extensive range of IaaS and PaaS offerings; used extensively by big businesses and startups.
- Microsoft Azure: Famed for ease of integration with Microsoft software and services, such as Windows Server and Active Directory.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Famous for data analysis, machine learning capabilities, and high-performance computing.

All of these platforms have free tiers and learning paths that can be used by beginners to familiarize themselves with hands-on experience.
Cloud Certifications for Beginners
Certifications are a great method to confirm cloud knowledge and prove technical capabilities to employers. The certifications listed below are highly suggested for beginners:
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner
- Microsoft Azure Fundamentals (AZ-900)
- Google Cloud Digital Leader
These certifications include essential cloud principles, pricing models, security, and compliance and are excellent stepping stones for beginners to cloud computing.
Security in the Cloud
Data security is one of the most prevalent issues regarding cloud computing. Although strong security models are employed by cloud providers, their customers also need to learn about shared responsibility models.
In a shared responsibility model:
- The infrastructure is secured by the cloud provider.
- Data, user access, and configurations must be secured by the user.
Newbies must start with security best practices like multi-factor authentication (MFA), role-based access control (RBAC), encryption, and periodic audits.
Getting Started in Cloud Computing
For newbies, beginning in cloud computing can be exhilarating yet daunting. Here’s an actionable guide:
Learn the Basics
Start with learning fundamental concepts, service models, and deployment models. Use tools such as VERSAtile Reads for easy learning.
Select a Cloud Provider
Pick one of the big three providers and sign up for a free-tier account to begin experimenting.
Finish Foundational Training
Take starter courses, documentation, and tutorials from AWS, Azure, or GCP.
Practise What You Know
Spawn virtual machines, construct basic applications, or host static websites to solidify what you know.
Pursue Certification
Prepare for and sit a foundation certification exam to authenticate your learning and unlock career prospects.
Conclusion
Cloud computing is transforming how technology works in business. For newbies, learning cloud basics is an important starting point to a myriad of career prospects and technical knowledge. Through its flexibility, scalability, and accessibility, cloud computing enables people and businesses to innovate and expand.
FAQs
1. What is the optimal cloud service model to learn first for beginners?
It’s advisable to begin with Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) since it introduces the core knowledge of virtual machines, storage, and networking, which are the foundational components of cloud infrastructure.
2. Do we require a technical foundation to learn cloud computing?
No. Most beginners have no technical background. With guided resources and hands-on experience, anyone can learn cloud computing, particularly through entry-level certifications.
3. What cloud certification should we get as a beginner?
AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner, Microsoft Azure Fundamentals (AZ-900), and Google Cloud Digital Leader are all great places to start. They give a general overview of cloud concepts and services without any extensive technical knowledge.
- Published Date:



