
Cloud Computing Demystified: Key Concepts and Certification Resources at VERSAtile Reads

Introduction
Cloud computing has emerged as a revolutionary technology, transforming how individuals and organizations manage, store, and interact with data. By providing flexible, scalable, and cost-effective solutions, cloud computing is now a cornerstone of modern business operations. Major platforms such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) lead the charge, enabling users to access powerful computing resources on demand.
Ready to elevate your cloud computing skills? VERSAtile Reads offers a comprehensive range of resources, from practice questions to exam cram notes, tailored to support both beginners and experienced IT professionals. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to validate advanced skills, VERSAtile Reads provides the tools you need to navigate the cloud landscape confidently. Visit VERSAtile Reads today to find the certification resources that align with your career goals and start your learning journey toward success in the world of cloud technology!
What is Cloud Computing?
At its core, cloud computing delivers various services over the internet. These include data storage, databases, networking, software applications, and analytics. By leveraging cloud technologies, organizations can avoid the significant upfront costs of maintaining physical infrastructure, such as servers and data centers. Instead, they can utilize cloud services based on their needs, leading to substantial cost savings and enhanced operational flexibility.
Cloud Computing Operates on Several Fundamental Principles:
- On-Demand Self-Service: Users can provision computing resources as needed without requiring human interaction with service providers.
- Broad Network Access: Cloud services are accessible from various devices, including smartphones, tablets, and laptops.
- Resource Pooling: Providers use a multi-tenant model to serve multiple customers from the same physical resources, optimizing efficiency.
- Rapid Elasticity: Resources can be scaled quickly based on demand, giving organizations agility.
- Measured Service: Cloud systems automatically control and optimize resource use, ensuring users are billed based on consumption.
These principles highlight the advantages that cloud computing brings to businesses and individuals.
Types of Cloud Computing Models
Understanding the primary service models of cloud computing is crucial for leveraging its full potential. There are three main types:
-
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides fundamental computing resources such as virtual machines, storage, and networks on a pay-as-you-go basis. Organizations can build and manage their IT infrastructures without investing heavily in physical hardware. This model is ideal for businesses that require scalable and customizable environments, as it allows them to adapt their resources based on evolving needs.
Key Features of IaaS:
- Scalability: Quickly adjust computing power and storage as needed.
- Control: Greater control over the operating systems and applications running on the infrastructure.
- Cost Efficiency: Pay only for what you use, making it easier to manage budgets.
-
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides a development platform that includes operating systems, databases, and development tools. This model simplifies the application development process, enabling developers to focus on writing code rather than managing the underlying infrastructure.
Key Features of PaaS:
- Development Tools: Offers built-in tools for application development and deployment.
- Collaboration: Facilitates collaboration among distributed development teams.
- Integrated Services: Allows easy integration with databases and middleware.
-
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers full-featured applications over the internet, eliminating the need for users to install or maintain software on their devices. This model is particularly beneficial for end-users who require access to applications without the complexities of infrastructure management.
Key Features of SaaS:
- Accessibility: Users can access applications from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Automatic Updates: Providers manage software updates and security, ensuring users always have the latest version.
- Subscription Model: Users typically pay a subscription fee, reducing upfront costs.
Types of Cloud Deployments
The choice of cloud deployment model significantly impacts scalability, cost, and security. Here are the main types:
-
Public Cloud
Public clouds are hosted by third-party providers and accessible to multiple users. They are delivered over the internet and offer shared resources, making them an attractive option for businesses that need flexibility and cost efficiency. Popular public cloud providers include AWS, Azure, and GCP.
Advantages:
- Cost-Effective: Users only pay for their consumption, eliminating large upfront investments.
- High Availability: Public cloud services are designed to be available at all times, with built-in redundancy.
-
Private Cloud
Private clouds consist of dedicated infrastructure for a single organization. This model offers enhanced control over security and compliance, particularly suitable for businesses with strict regulatory requirements.
Advantages:
- Customization: Organizations can tailor the environment to meet specific needs.
- Improved Security: Greater control over data and applications reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
-
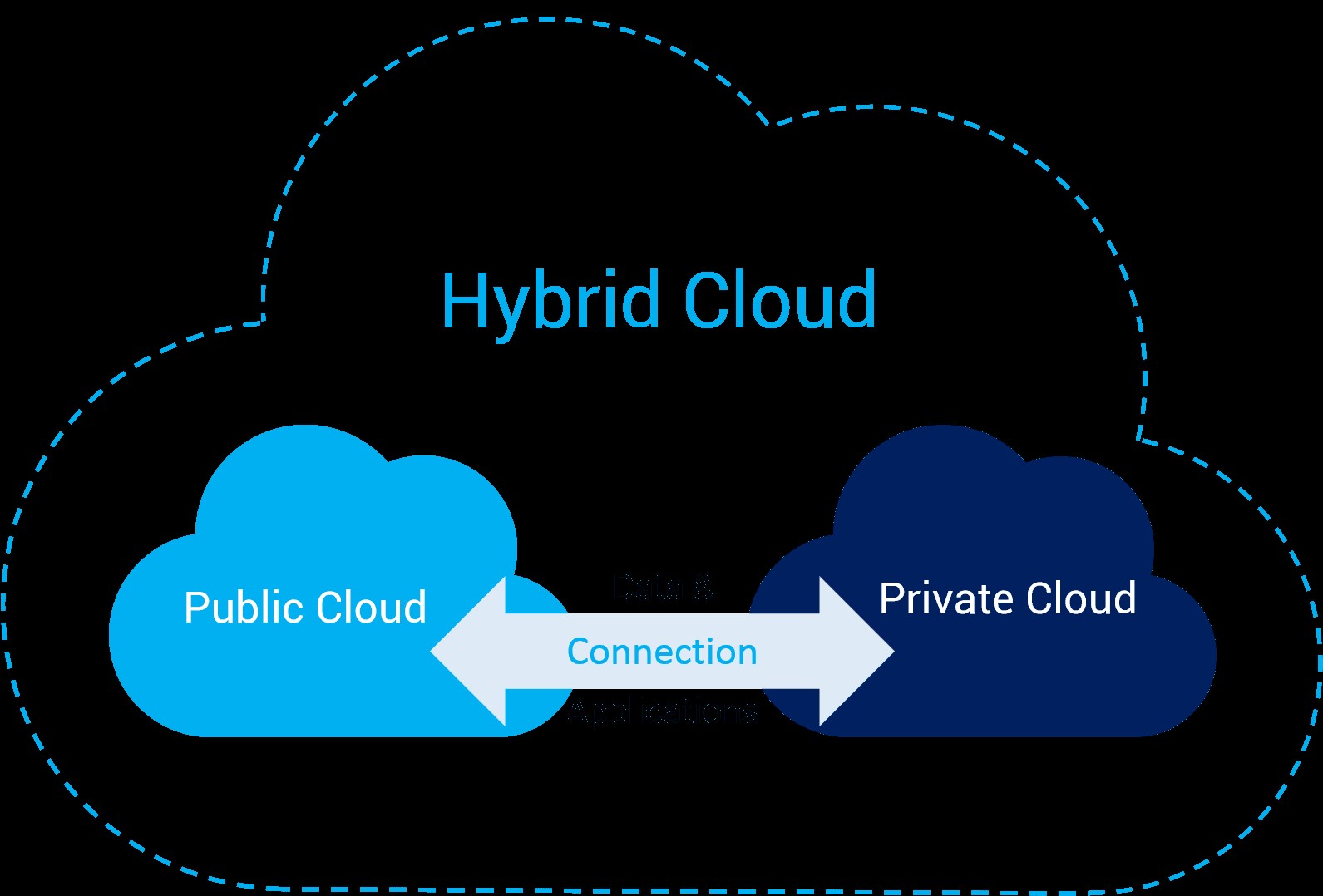
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud models combine public and private clouds, allowing for flexible data sharing and optimized scalability. This approach balances a private cloud’s control with a public cloud’s cost benefits.
Advantages:
- Flexibility: Organizations can choose where to run their applications based on specific needs.
- Optimized Performance: Workloads can be balanced between public and private environments for efficiency.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing brings numerous benefits that transform how businesses operate:
-
Cost Savings
By utilizing cloud services, businesses can avoid significant capital expenditures on physical infrastructure. The pay-as-you-go model allows organizations to pay only for the resources they use, making budget management easier.
-
Scalability
Cloud solutions enable organizations to scale their resources up or down based on demand quickly. This is particularly valuable for businesses with fluctuating workloads, such as e-commerce sites, during peak shopping seasons.
-
Data Backup and Recovery
Cloud providers often include automated backup processes that protect data across multiple locations. This ensures reliable data recovery in case of data loss or system failure.
-
Collaboration and Accessibility
Cloud computing allows employees to access data and applications from anywhere, fostering remote collaboration and enhancing productivity. This capability is especially crucial in today’s increasingly remote work environment.
-
Environmental Sustainability
By optimizing resource usage and reducing the need for physical infrastructure, cloud computing can contribute to environmental sustainability. Many cloud providers are committed to using renewable energy sources for their data centers.
Cloud Security Essentials
As more organizations adopt cloud solutions, security becomes a top priority. Key focus areas include:
-
Data Protection
Implementing robust data protection measures, such as encryption and data loss prevention (DLP), is critical to safeguarding sensitive information stored in the cloud.
-
Access Control
Establishing strict access controls ensures that only authorized users can access cloud resources. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access control (RBAC) are effective strategies for enhancing security.
-
Regulatory Compliance
Organizations must ensure their cloud practices comply with relevant regulations, such as GDPR or HIPAA. Regular audits and assessments can help identify and mitigate compliance risks.
-
Continuous Monitoring
Employing security monitoring tools can help detect and respond to potential threats in real-time, enhancing the overall security posture of cloud environments.
Why Get Certified?
Pursuing cloud certifications offers numerous advantages:
- Career Advancement: Certifications enhance your resume and can open doors to new job opportunities.
- Improved Job Prospects: Many employers prioritize certified candidates when hiring for cloud-related roles.
- Enhanced Credibility: Certifications validate your expertise and can boost your confidence in your skills.
- Staying Competitive: As cloud adoption continues to rise, having relevant certifications positions you favorably in the job market.
Certification Resources Available at VERSAtile Reads
Certification can validate your skills and knowledge and give you a competitive edge in cloud computing. VERSAtile Reads offers a range of certification resources designed to support your learning journey in cloud technology.
-
Microsoft Azure Fundamentals (AZ-900)
The AZ-900 certification introduces learners to the basics of Microsoft Azure, making it ideal for those looking to demonstrate their foundational knowledge of Azure services, cloud concepts, and basic compliance and security principles.
- Cloud Concepts: Understanding cloud computing principles, types of cloud services (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS), and cloud deployment models (public, private, hybrid).
- Azure Core Services: Familiarity with core Azure services like Azure Compute, Storage, Networking, and databases.
- Security and Compliance: Basics of Azure security features, governance, compliance frameworks, and the Azure Security Center.
- Azure Pricing and Support: Understanding pricing models, cost management tools, and available support options.
- Target Audience: This certification is suited for anyone looking to start a career in cloud services, including non-technical roles such as sales, marketing, and project management.
-
AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner
The AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner certification provides foundational knowledge of AWS cloud services and basic concepts designed for individuals with a general understanding of the AWS platform.
- Cloud Concepts: Similar to AZ-900, this includes fundamental cloud principles, benefits, and types of cloud services.
- AWS Core Services: Familiarity with key AWS services, including compute (EC2), storage (S3), databases (RDS), and networking (VPC).
- Security and Compliance: Overview of AWS security best practices, identity and access management (IAM), and compliance programs.
- Billing and Pricing: Understanding AWS pricing models, billing methods, and cost management tools.
- Target Audience: This certification is intended for individuals looking to build a foundational understanding of AWS, including business professionals, project managers, and newcomers to cloud technology.
-
AZ-104: Microsoft Azure Administrator
The AZ-104 certification is aimed at Azure administrators. It validates your ability to manage Azure resources, implement and manage storage solutions, configure virtual networks, and ensure security and compliance within the Azure environment. Key areas of focus include:
- Managing Azure Identities and Governance: It includes managing Azure Active Directory, role-based access control (RBAC), and subscriptions.
- Implementing and Managing Storage: Understanding how to manage storage accounts, blob storage, and file shares.
- Deploying and Managing Azure Compute Resources: This covers managing virtual machines, Azure Kubernetes Service, and Azure App Services.
- Configuring and Managing Virtual Networking: Knowledge of Azure networking, including VPNs and Network Security Groups (NSGs).
- Monitoring and Backing Up Azure Resources: Using Azure Monitor, Log Analytics, and Azure Backup.
-
Google Certified Professional Cloud Architect
In contrast, the Google Certified Professional Cloud Architect certification focuses on the Google Cloud Platform (GCP). It demonstrates your ability to design, develop, and manage robust, secure, scalable, and highly available GCP solutions. Key areas of focus include:
- Designing and Planning Cloud Solutions: Understanding how to design cloud architectures based on requirements.
- Managing and Provisioning GCP Resources: Proficiency in managing virtual machines, Kubernetes, and serverless architectures.
- Security and Compliance: Implementing security best practices, IAM, and compliance frameworks.
- Optimizing Technical Solutions: Analyzing workloads and optimizing performance and cost.
- Monitoring and Managing Solutions: Using tools like Operations Suite for logging and monitoring.
Conclusion
Cloud computing is no longer just an emerging technology; it has become essential to modern business strategy. Understanding the fundamental concepts and obtaining relevant certifications are crucial for anyone looking to harness the power of the cloud. VERSAtile Reads provides a wealth of resources to help you build your skills, whether you’re just starting or looking to advance your career.
By investing in cloud education and certification, you can position yourself as a valuable asset in an increasingly competitive job market. The future of work is in the cloud, and with the right knowledge and credentials, you can thrive in this dynamic environment.
FAQs
-
Why is cloud computing important in today’s business environment?
Cloud computing enables businesses to cut costs, improve efficiency, and enhance flexibility, ensuring they remain competitive and innovative in a digital era.
-
What are the primary differences between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS?
IaaS offers raw computing resources, PaaS provides platforms for development, and SaaS delivers full applications over the internet. Each serves distinct organizational needs.
-
How long does it typically take to get a cloud certification?
Duration varies based on the certification type and prior experience. Foundation-level certifications may take 1–3 months, while advanced certifications might require 6 months or more of dedicated study.
- Published Date:



